NIGMS actively supports efforts to catalyze the modernization of biomedical graduate education. We have undertaken a number of initiatives to stimulate this process, including hosting a symposium to showcase innovations in biomedical graduate education and providing administrative supplements to T32 predoctoral training grants to enhance rigor and reproducibility, career development and skills development.
On June 8, 2016, we took another step to encourage such change with the release of a Request for Information (RFI) seeking input on how our institutional predoctoral training grants program can be used to promote innovations in training. The RFI asked members of the community to weigh in on the strengths and weaknesses of the current system, the skills the next generation of graduate students should acquire, barriers to change and strategies to promote change through our institutional predoctoral research training grants.
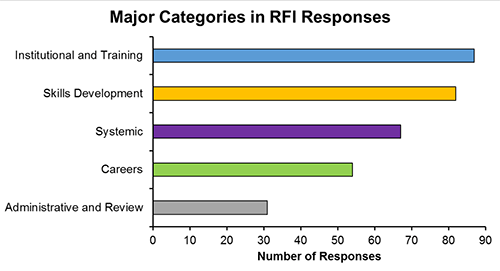
We received 90 unique responses from stakeholders ranging from students and faculty to institutions and professional societies. Themes represented in the responses were organized around five major categories:
- Institutional and training-related issues,
- Skills development,
- Systemic issues within the research enterprise,
- Careers, and
- Administrative and review issues.
While NIGMS recognizes that those who responded to the RFI are unlikely to represent a random subset of the individuals and organizations who have a stake in graduate biomedical education, these responses provide insights regarding how members of the extramural community view the current challenges and opportunities in graduate biomedical education. As such, these comments will inform NIGMS’ ongoing efforts to catalyze the modernization of graduate education through a new predoctoral T32 funding announcement, which is currently under development. For more details about the analysis, we encourage you to explore the report.