I recently described the role that an advisory council plays as the second level of peer review for applications submitted to NIH. One thing that neither advisory councils nor study sections do, however, is make funding decisions. How, then, are these decisions made?
In this post, I’ll describe the process we use at NIGMS.
The Institute is organized into five units: four divisions (Cell Biology and Biophysics; Genetics and Developmental Biology; Minority Opportunities in Research; and Pharmacology, Physiology, and Biological Chemistry) and a center (Bioinformatics and Computational Biology). Once the National Advisory General Medical Sciences Council has met, each unit organizes meetings (referred to as “paylist meetings”) attended by most or all of the program directors within that unit.
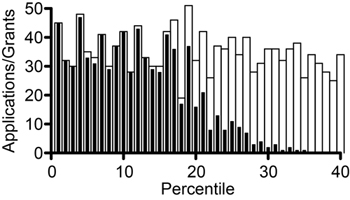
During a paylist meeting, applications are discussed and prioritized, beginning with the top-scoring applications. These applications (typically up to about half of the number that are expected to be funded) are given highest priority for funding unless there are specific issues, such as those related to the NIGMS well-funded laboratory policy or other concerns that came up at the Council meeting.
The discussion then turns to applications in the “gray area,” typically extending to about 10 percentile points beyond where we would expect to be able to fund applications if they were awarded in straight percentile order. Each application is discussed, typically in percentile order, although sometimes early-stage investigators (ESIs) are discussed first.
For each application, the responsible program director presents the scientific topic as well as factors such as whether the applicant is an ESI or new investigator, how much other support the applicant has (particularly if the application represents the only support available to the investigator), whether the Council has given us specific advice on the application, whether the scientific area is perceived to be particularly exciting, and how much other research we already support in the general area of the application. The other members of the unit listen to these presentations, and the group then produces a prioritized list of applications.
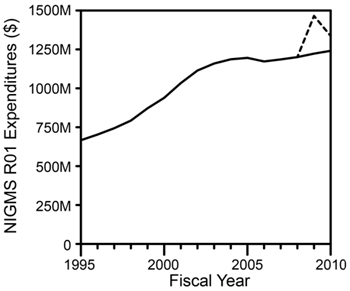
The other key factor for final funding decisions is, of course, the availability of funds. Funds are provided through the appropriations process, either through a regular appropriations bill or, sometimes toward the beginning of a fiscal year, a continuing resolution that typically funds government programs at the previous year’s level. When it is reasonably clear what level of funds is available at a particular point in the fiscal year, the funds are allocated to different mechanisms and programs (research project grants, training grants, various programs within the Division of Minority Opportunities in Research, and so on) based on our previously established budget. Funds for unsolicited R01s are allocated among the four units within NIGMS that fund these applications (the Divisions of Cell Biology and Biophysics; Genetics and Developmental Biology; and Pharmacology, Physiology, and Biological Chemistry; and the Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology), based on the fractions of applications that have scored well enough to be considered for possible funding.
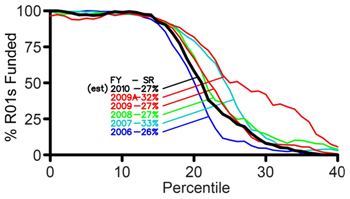
Paylists are then developed using the prioritized lists, with budget adjustments for each application based on NIH and NIGMS-wide policies as well as considerations specific to the application provided by the responsible program director. Applications are paid until the available funds are exhausted. Applications that are relatively high on the priority list but could not be funded with a given allocation are flagged for consideration later in the fiscal year, when more funds may become available. This process leads, over the course of a full fiscal year, to the funding curves we recently posted.
 An important step in the annual budget process is the release of the President’s budget request, which happened yesterday. The NIGMS slice is detailed in our FY 2012 budget justification, which includes a budget mechanism table, budget graphs, a Director’s overview and a justification narrative.
An important step in the annual budget process is the release of the President’s budget request, which happened yesterday. The NIGMS slice is detailed in our FY 2012 budget justification, which includes a budget mechanism table, budget graphs, a Director’s overview and a justification narrative.

 In March 2010, I announced that we were in the process of developing a strategic plan for research training, and I asked for your input.
In March 2010, I announced that we were in the process of developing a strategic plan for research training, and I asked for your input. NIH recently launched a new site for communication with the scientific community, http://feedback.nih.gov/. The site has already been quite active, since it requests input on a proposed National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) and a proposed institute focused on substance use, abuse and addiction research.
NIH recently launched a new site for communication with the scientific community, http://feedback.nih.gov/. The site has already been quite active, since it requests input on a proposed National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) and a proposed institute focused on substance use, abuse and addiction research.