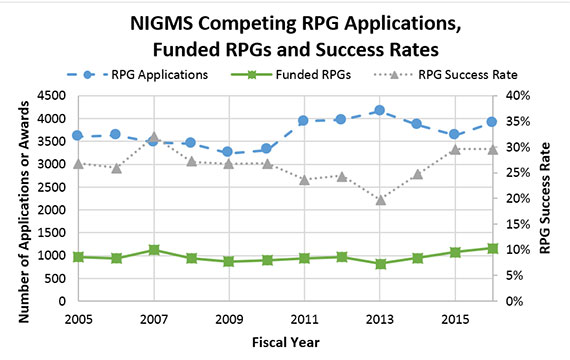
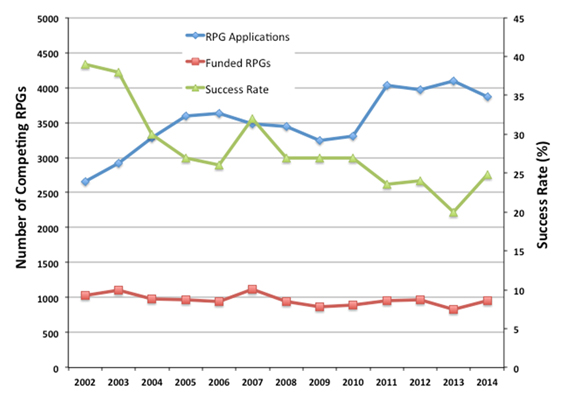
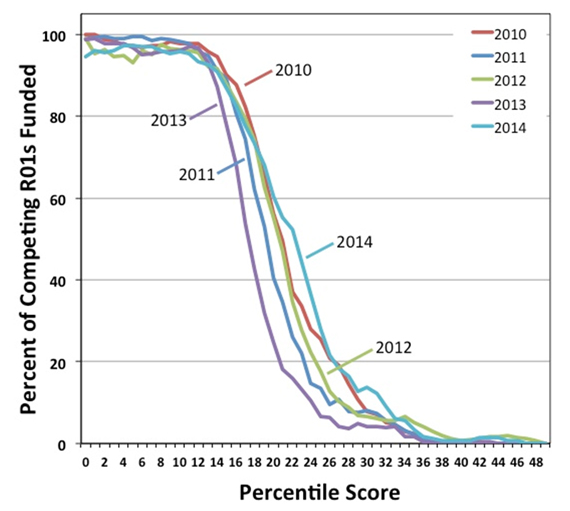
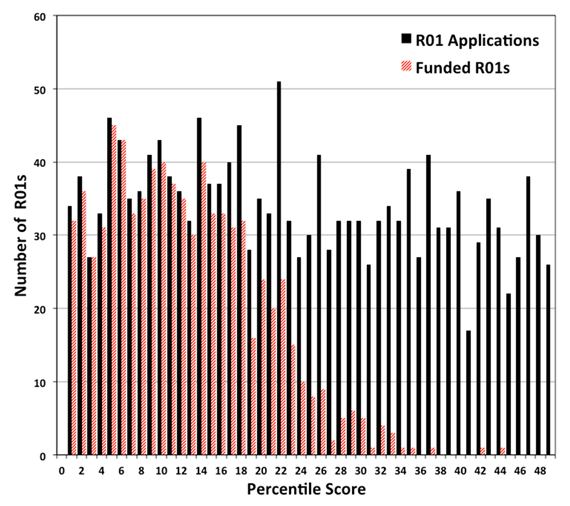
Our Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award (MIRA) program is still relatively new, so it’s not surprising that NIGMS staff frequently hear misconceptions about it. This post dispels five common MIRA myths.
Myth 1: Once an investigator is awarded a MIRA, the budget will never increase.
MIRA budgets may increase. At the time of the competing renewal application, a principal investigator (PI) may request an increase in funding. MIRAs with modest budgets that have been very productive and score very well could receive budget increases. Study sections will be asked to look at budget requests, and NIGMS staff will make determinations based on the reviewers’ recommendations and available funds.
Myth 2: Early stage investigators will receive more funding for their labs if they get an R01 than if they get a MIRA.
A MIRA PI who is an early stage investigator (ESI) has a higher probability of receiving more NIGMS funding than a non-MIRA ESI. Most ESI MIRA investigators receive $250,000 in direct costs per year. A recent analysis found that the vast majority of ESIs who have received an NIGMS R01 are initially awarded $200,000 or less, and most do not go on to receive a second NIGMS R01 during the first five years of their initial award. Thus, the total NIGMS funding for most relatively new investigators is higher with a MIRA.
Myth 3: MIRA discourages collaborative research.
NIGMS strongly endorses collaborative research, and this extends to the MIRA program. However, the MIRA concept is based on the idea that NIGMS will provide support to individual investigators’ research programs. Collaborators are expected to work together because of their mutual interest in a problem. The collaborator, in most cases, will support his or her efforts with independent funding, not through a subcontract from the MIRA. In cases where a collaborator’s efforts are well-justified, essential to the research program of the MIRA and cannot be supported by the collaborator, a consortium agreement can be included in the competing application.
NIGMS also encourages scientifically productive international collaborative research efforts. However, NIGMS will only provide funding for a foreign consortium arrangement when the collaboration is essential to the PI’s research program, represents a unique scientific opportunity and cannot be supported by the collaborator.
Myth 4: MIRA PIs cannot apply for administrative supplements.
MIRA PIs are eligible for Research Supplements to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research and may be eligible for other types of administrative supplements, such as equipment supplements offered by NIGMS through notices in the NIH Guide for Grants and Contracts. In rare situations, NIGMS may provide a supplement for a piece of equipment that could not have been anticipated at the time the application was submitted.
Myth 5: MIRA PIs cannot apply for NIGMS training grants or conference grants.
MIRA PIs are eligible to apply for grants that support research resources, training, workforce development or diversity building, clinical trials, selected cooperative agreements, SBIR/STTRs, conference grants and the portion of a center grant or a P01 that is strictly a core. In addition, a MIRA PI may receive grants from other NIH institutes or centers, although when making funding decisions NIGMS always considers an investigator’s other support, as described on our Funding Policies page.
More information, including answers to frequently asked questions, is on the MIRA page.